Turbocharger vs. Supercharger: The Basics of Forced Induction
Forced induction has revolutionized the automotive industry, providing a significant boost in power and performance for engines. Two common methods of forced induction are turbocharging and supercharging.
Both systems have their merits, but they operate differently and offer distinct advantages. In this article, we will delve into the basics of turbochargers and superchargers, exploring their functionality, benefits, and considerations. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or simply curious about engine technology, understanding these two forced induction systems will give you valuable insights into the world of high-performance engines.
Turbocharger:
How a Turbocharger Works:
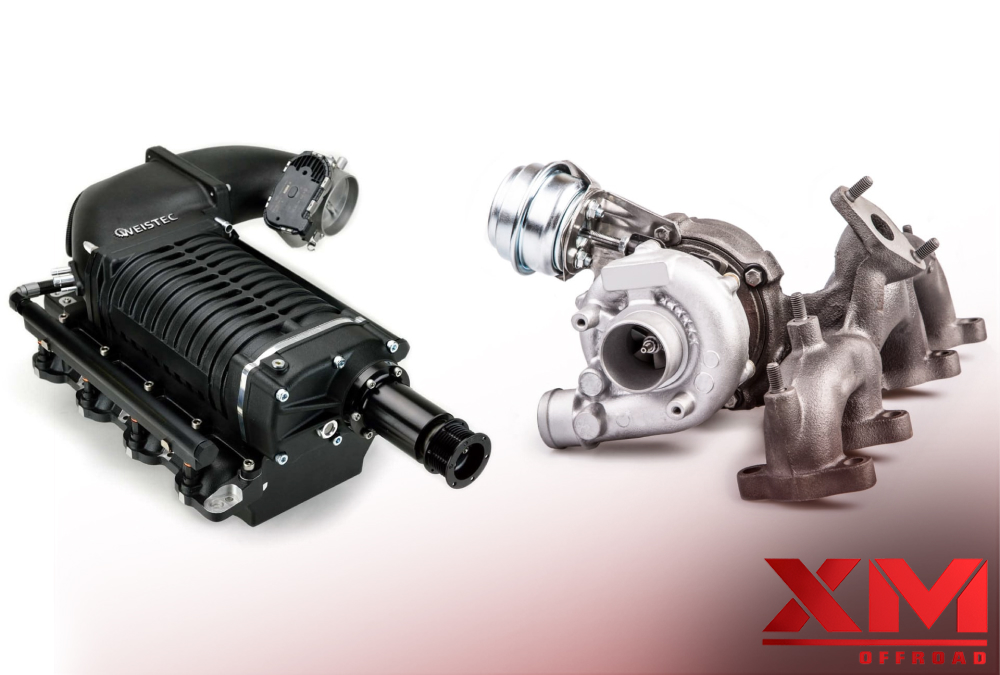
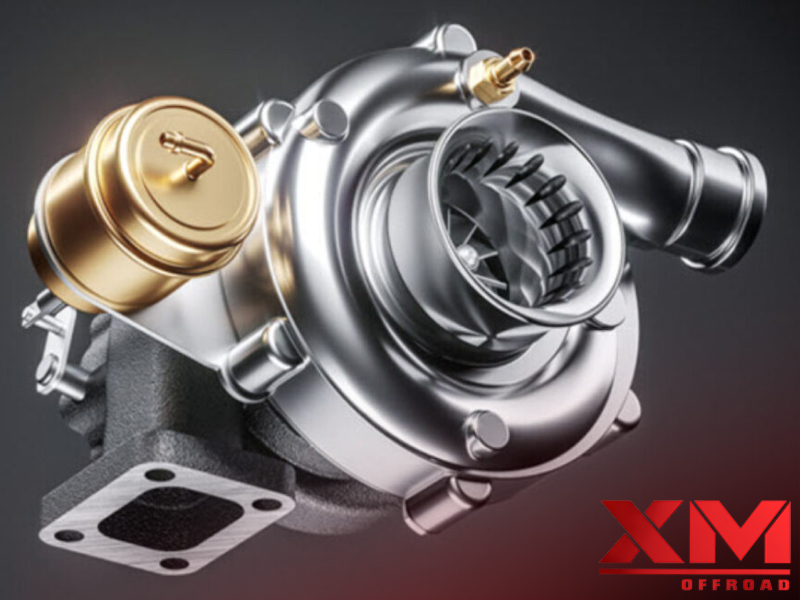
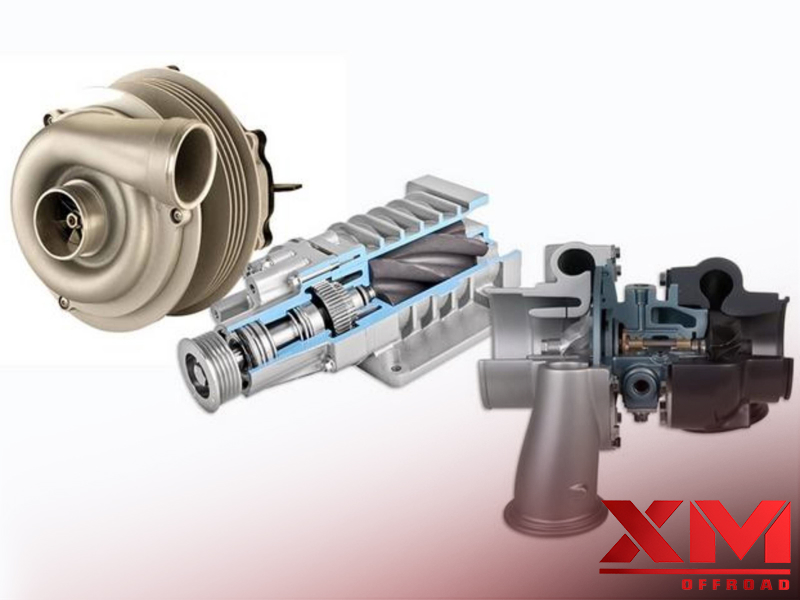
A turbocharger is a device that utilizes the energy from an engine’s exhaust gases to enhance its performance. It consists of two main components: a turbine and a compressor. The exhaust gases exit the engine’s combustion chambers and enter the turbocharger’s turbine housing. Inside the housing, the exhaust gases pass through a series of curved blades, known as the turbine wheel. As the hot gases flow over the turbine wheel, they cause it to rotate at high speeds.
The turbine wheel is connected to a shaft, and on the opposite end of the shaft is the compressor wheel, housed in the compressor housing. As the turbine wheel spins, it transfers rotational energy to the compressor wheel. The compressor wheel has its own set of curved blades, which draw in ambient air through the air filter. As the compressor wheel rotates, it compresses the incoming air, increasing its pressure and density.
The pressurized air, now at a higher temperature and density, is discharged from the turbocharger’s outlet and enters the engine’s intake manifold. In the intake manifold, the compressed air mixes with the appropriate amount of fuel. The increased air density allows for a more efficient combustion process, as more fuel molecules are available for burning. This results in improved power output from the engine.
To maintain the turbocharger’s optimal performance and prevent damage, various components are integrated into the system. An intercooler is typically employed to cool down the compressed air before it enters the engine, increasing its density and further enhancing combustion efficiency. Additionally, a wastegate is utilized to regulate the boost pressure generated by the turbocharger, preventing it from exceeding safe levels.
Advantages of Turbocharging:
Turbochargers offer several advantages, making them a popular choice in modern engines.
Increased Power:
By effectively utilizing exhaust gas energy, turbochargers can significantly boost engine power output without increasing engine displacement.
Improved Fuel Efficiency:
Turbocharged engines can achieve better fuel efficiency since they can extract more power from a given amount of fuel.
High Altitude Performance:
Turbochargers can compensate for the loss of atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes, ensuring consistent power delivery in diverse conditions.
Packaging and Retrofitting:
Turbochargers are typically compact, allowing easier installation in existing engine bays and providing flexibility for engine upgrades.
Considerations with Turbocharging:
Despite their advantages, turbochargers have a few considerations that need to be addressed:
Turbo Lag:
Turbochargers suffer from a phenomenon called “turbo lag,” which is the delay in boost response due to the time taken for the exhaust gases to spin the turbine wheel. However, advancements in technology have significantly reduced this lag in modern turbocharged engines.
Complexity:
Turbocharger systems are more complex compared to superchargers, with additional components such as intercoolers, wastegates, and blow-off valves. This complexity can increase maintenance requirements and costs.
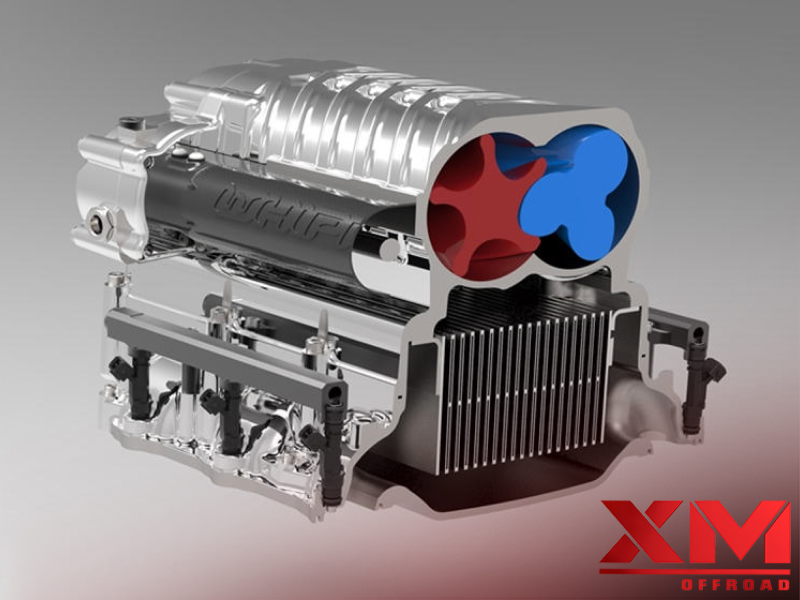
Supercharger:
A supercharger is a mechanical compressor that is driven directly by the engine, typically using a belt connected to the crankshaft. As the engine turns, the supercharger’s compressor draws air and compresses it before supplying it to the engine’s intake manifold. By increasing the air pressure, the supercharger allows more oxygen to enter the combustion chamber, resulting in increased power output.
Advantages of Supercharging:
Superchargers offer distinct advantages that make them a popular choice for certain applications:
- Instant Boost: Unlike turbochargers, superchargers deliver instant boost response since they are directly driven by the engine and do not rely on exhaust gases.
- Linear Power Delivery: Superchargers provide a more linear power delivery, without the inherent lag present in turbochargers.
- Simple Design: Supercharger systems are generally simpler compared to turbochargers, with fewer components involved. This simplicity can result in lower maintenance costs and easier installation.
Considerations with Supercharging:
Superchargers also have a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Increased Engine Load: Superchargers draw power from the engine to drive the compressor, creating additional load on the engine. This increased load can affect fuel efficiency and overall engine durability.
- Limited Efficiency at Higher RPM: Superchargers can become less efficient at high engine speeds due to the increased parasitic load on the engine. This limitation can impact top-end power potential.
The Impact of Forced Induction on Wheel Upgrades | Get XM Off-road Rims
When considering forced induction systems like turbochargers or superchargers, it’s important to account for their potential impact on wheel upgrades.
One common modification for car enthusiasts is upgrading to larger alloy rims, such as 20-inch wheels, to enhance the vehicle’s appearance and performance.
However, it’s crucial to ensure that the forced induction system is compatible with these wheel upgrades. The increased power output and torque generated by forced induction can place additional stress on the wheels and tires.
Therefore, it’s recommended to consult with a knowledgeable mechanic or tuner to ensure that the 20 inch alloy rims are adequately reinforced to handle the increased forces associated with forced induction, maintaining both performance and safety.
Tire Selection Considerations for Forced Induction Applications
In forced induction applications, the choice of tires becomes even more crucial. The increased power and torque delivered by turbochargers or superchargers require tires that can effectively transfer that power to the ground while maintaining traction and stability.
When upgrading to 20-inch alloy rims, it’s essential to select tires with the appropriate specifications to handle the increased performance.
Look for tires with a higher load rating to support the additional weight and dynamic forces associated with forced induction. Additionally, consider tires with a suitable speed rating to ensure they can handle the higher speeds that may be achieved with the increased power output.
Proper tire selection will help maximize the benefits of forced induction while providing optimal handling and grip for a safer and more exhilarating driving experience.
Conclusion:
Both turbochargers and superchargers offer unique advantages and considerations for forced induction.
Turbochargers excel in providing high power and improved fuel efficiency, especially at higher altitudes. Superchargers, on the other hand, offer instant boost response and linear power delivery.
The choice between the two depends on specific requirements, such as desired power characteristics, packaging constraints, and intended application.
Read Also: Toyota RAV4 Adventure: How Much Can You Tow and Exploring its Performance?
Ultimately, forced induction technologies continue to evolve, and advancements in both turbochargers and superchargers are enabling manufacturers to extract more performance from engines while addressing previous limitations.
FAQs:
Q1) What is forced induction?
Forced induction is a method used to increase an engine’s power output by compressing the intake air, resulting in improved combustion and greater performance.
Q2) How does a turbocharger work?
A turbocharger uses exhaust gases to power a turbine, which drives a compressor. The compressor forces more air into the engine, allowing for increased fuel combustion and power output.
Q3) What are the advantages of turbocharging?
Turbocharging offers increased power, improved fuel efficiency, high altitude performance, and packaging flexibility for engine upgrades.
Q4) What is turbo lag?
Turbo lag refers to the delay in boost response caused by the time taken for the exhaust gases to spin the turbine wheel. Modern advancements have significantly reduced turbo lag in newer turbocharged engines.
Q5) How does a supercharger work?
A supercharger is mechanically driven by the engine and compresses the intake air directly. It provides instant boost response and linear power delivery without the lag associated with turbochargers.
Q6) What are the considerations with supercharging?
Superchargers increase engine load and can affect fuel efficiency and engine durability. They may also become less efficient at higher engine speeds due to the additional load placed on the engine.